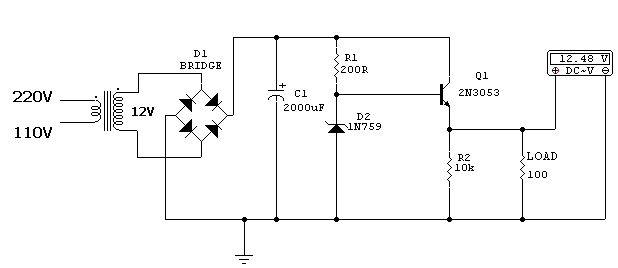
12V DC Power Supply Using 2N3053
This simple 12V DC power supply converts 220V AC mains into a stable 12V DC output. It uses a rectifier bridge for AC to DC conversion, a 2N3053 transistor for current amplification, and a 1N759 Zener diode for voltage regulation.
Power Supply Requirements
- The mains AC (220V or 110V) is stepped down to 12V AC using a suitable transformer.
- A rectifier bridge converts AC to pulsating DC.
- Filter capacitors smooth the DC voltage for stable output.
Key Components
- 2N3053 Transistor: Acts as a pass transistor to handle higher load currents and provide current amplification.
- 1N759 Zener Diode: Provides voltage regulation to maintain a stable 12V output.
- Rectifier Bridge: Converts AC from transformer to DC for regulation.
- Filter Capacitors: Smooth the rectified DC to reduce ripple voltage.
- Transformer (220V to 12V AC): Steps down the mains voltage to a safer level for the circuit.
Circuit Operation
- The 220V AC mains is stepped down to 12V AC by the transformer.
- The rectifier bridge converts 12V AC to unregulated DC voltage.
- The 1N759 Zener diode sets a reference voltage for the 2N3053 transistor.
- The 2N3053 transistor amplifies the current and supplies a stable 12V DC to the load.
- Filter capacitors smooth the output, minimizing ripple for connected devices.
Key Features
- Stable 12V DC output from 220V AC mains
- Uses 2N3053 transistor for higher current capability
- Zener diode (1N759) ensures voltage regulation
- Simple transformer and rectifier bridge design
- Compact and low-cost solution for small 12V DC loads
Construction Notes
- Ensure correct orientation of the rectifier diodes and Zener diode to prevent circuit damage.
- Mount the 2N3053 transistor on a heatsink if high currents are expected.
- Use adequately rated filter capacitors for the load current to minimize voltage ripple.
- Verify the transformer output under load to ensure proper regulation.
- Test the power supply with a dummy load before connecting sensitive devices.